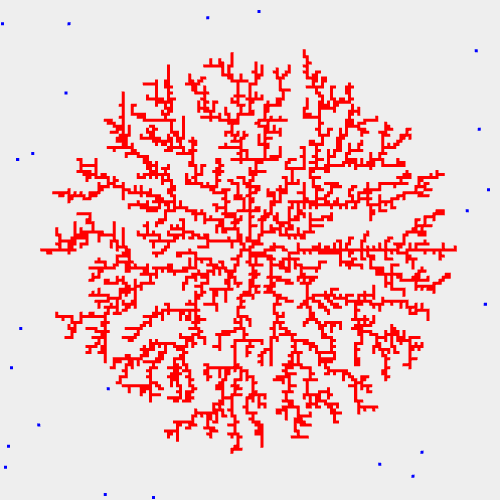
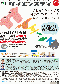雪の結晶シミュレーション(2次元DLA)
【アルゴリズム】水分子(水色)の運動をランダムウォークとみなしランダムな位置からスタートさせます。 中心部分にある核(赤)に接触すると、水分子は吸着して固まります。 固まった後は、核と同様に水分子を吸着していく。 その結果、数珠繋ぎに成長していくことになります。
本シミュレーションは拡散律則凝集と呼ばれ、結晶成長の単純なモデルとして考えられています。
参考:DLAによる樹木状クラスタのシミュレーション、DLAによる樹木状クラスタのフラクタル次元
プログラムソース(HTML5, JavaScript)
//////////////////////////////////////////////
// 雪の結晶シミュレーション
//////////////////////////////////////////////
//DLAクラス
var DLA2D = function () {
//粒子数
this.N = 20000;
//初期位置の最小値
this.L0 = 100;
//初期位置の最大値
this.Lmax = 500;
//内部プロパティ
this.perticles = []; //粒子情報が格納される配列
this.fixPerticleIndex = []; //吸着された粒子インデックスが格納される配列
this.maxLengthSq = 1; //原点からの最大距離の2乗
//形状オブジェクトの宣言と生成
this.geometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(1, 1);
//材質オブジェクトの宣言と生成
this.material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial( {color:0x0000FF} );
//材質オブジェクトの宣言と生成
this.fixedMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial( {color:0xFF0000} );
//初期化
this.init = function() {
//分布密度関数の係数
var A = 2 / ( this.L0*this.L0 + this.Lmax*this.Lmax );
for( var i = 0; i <= 100; i++ ) this.fixPerticleIndex[ i ] = [ ];
for( var n = 0; n < this.N; n++ ){
//積分分布密度
var F = Math.random();
//積分分布密度から得られる距離
var L = Math.sqrt( this.L0*this.L0 + 2 * F / A );
//偏角
var theta = 2 * Math.PI * Math.random();
var x = L * Math.cos( theta ) ;
var y = L * Math.sin( theta ) ;
x = Math.round(x);
y = Math.round(y);
//平面オブジェクトの生成
this.perticles[n] = new THREE.Mesh( this.geometry, this.material );
//初期値を指定
this.perticles[n].position.set( x, y, 0 );
//平面オブジェクトのシーンへの追加
scene.add( this.perticles[n] );
//固定フラグ
this.perticles[n].fixed = false;
}
//核を設定
this.perticles[0].position.set( 0, 0, 0 );
this.perticles[0].fixed = true;
this.fixPerticleIndex[ 0 ].push( 0 );
//描画色を変更
this.perticles[0].material = this.fixedMaterial;;
this.perticles[0].needsUpdate = true;
}
//時間発展
this.timeEvolution = function() {
var x, y, r, lengthSq;
return function() {
for( var i = 0; i < this.N; i++ ){
if( this.perticles[i].fixed ) continue;
x = this.perticles[i].position.x;
y = this.perticles[i].position.y;
r = Math.random();
if( r < 0.25 ) x += 1.0;
else if( r < 0.50 ) x -= 1.0;
else if( r< 0.75 ) y += 1.0;
else y -= 1.0;
this.perticles[i].position.x = x;
this.perticles[i].position.y = y;
lengthSq = x*x + y*y;
//吸着テスト
if( lengthSq <= this.maxLengthSq ) this.checkCollision( i , lengthSq);
}
}
}();
//吸着テスト
this.checkCollision = function ( n, lengthSq ){
var v = new THREE.Vector3();
var lengthIndex, M, index;
var i, j;
return function( n, lengthSq ){
//距離配列要素番号
lengthIndex = Math.floor( Math.sqrt( lengthSq ) );
for( j = lengthIndex - 1; j <= lengthIndex + 1; j++ ){
if( j < 0 ) continue;
M = this.fixPerticleIndex[ j ].length;
for( i = 0; i < M ; i++ ){
index = this.fixPerticleIndex[ j ][ i ];
lengthSq = v.copy( this.perticles[ n ].position ).sub( this.perticles[ index ].position ).lengthSq();
if( lengthSq <= 1.0 ) {
this.perticles[n].fixed = true;
this.fixPerticleIndex[ lengthIndex ].push( n );
//描画色を変更
this.perticles[n].material = this.fixedMaterial;
this.perticles[n].needsUpdate = true;
//最大半径の更新
if( this.perticles[ n ].position.lengthSq() >= this.maxLengthSq ) {
this.maxLengthSq = Math.pow( this.perticles[ n ].position.length() + 1, 2);
//console.log( this.maxLengthSq );
}
return;
}
}
}
}
}();
}