【GSLで数値計算7】
エルミート行列の固有値の固有ベクトル
本稿では、GSL(GNU科学技術計算ライブラリ)を用いてエルミート行列の固有値と固有ベクトルの計算を行うサンプルプログラムを示します。→ GNU科学技術計算ライブラリのインストール(Windows, VisualStudio2017)はこちら
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// エルミート行列の固有値の固有ベクトル
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
#include <gsl/gsl_math.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_blas.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_vector.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_matrix.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_eigen.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_sort_vector.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_complex.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_complex_math.h>
//行列の次元
const int DIM = 2;
int main(void) {
std::cout << std::setprecision(5);
//GSL複素数ベクトルのメモリ確保(固有ベクトル用)
gsl_vector_complex *eig_vec = gsl_vector_complex_alloc(DIM);
//GSL複素数ベクトルのメモリ確保(固有値ベクトル用)
gsl_vector *eig = gsl_vector_alloc(DIM);
//GSL複素数行列のメモリ確保(エルミート行列用)
gsl_matrix_complex *matrix = gsl_matrix_complex_alloc(DIM, DIM);
//GSL複素数行列のメモリ確保(固有ベクトルのまとめ行列用)
gsl_matrix_complex *eig_vecs = gsl_matrix_complex_alloc(DIM, DIM);
//エルミート行列の設定
gsl_matrix_complex *frank_a = gsl_matrix_complex_alloc(DIM, DIM);
gsl_complex A[DIM][DIM];
//GSL_SET_COMPLEX(&aa, 1.0, 0.0);
// A[0][0] = 1 + 0i
A[0][0] = { 1.0, 0.0 };
gsl_matrix_complex_set(frank_a, 0, 0, A[0][0]);
// A[0][1] = 1 - 1i
A[0][1] = { 1.0, -1.0 };
gsl_matrix_complex_set(frank_a, 0, 1, A[0][1]);
// A[1][0] = 1 + 1i
A[1][0] = { 1.0, 1.0 };
gsl_matrix_complex_set(frank_a, 1, 0, A[1][0]);
// A[1][1] = 2 + 0i
A[1][1] = { 2.0, 0.0 };
gsl_matrix_complex_set(frank_a, 1, 1, A[1][1]);
// 行列の表示
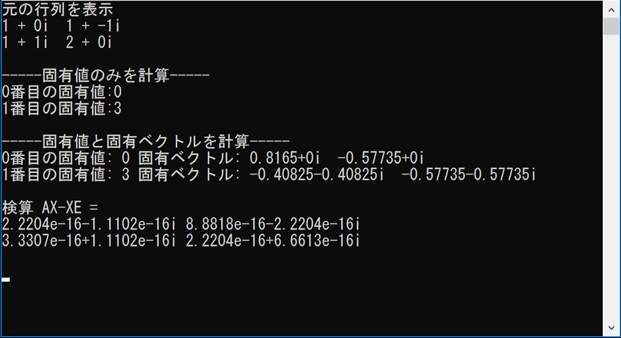
std::cout << "元の行列を表示" << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < DIM; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < DIM; j++) {
gsl_complex aa = gsl_matrix_complex_get(frank_a, i, j);
std::cout << GSL_REAL(aa) << " + " << GSL_IMAG(aa) << "i ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
/////////////////////////////////////////
// 固有値のみ計算
/////////////////////////////////////////
// 作業領域の確保
gsl_eigen_herm_workspace *workspace = gsl_eigen_herm_alloc(DIM);
// 行列のコピー
gsl_matrix_complex_memcpy(matrix, frank_a);
// 固有値の計算
gsl_eigen_herm(matrix, eig, workspace);
// 固有値の並び替え
gsl_sort_vector(eig);
std::cout << "-----固有値のみを計算-----" << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < DIM; i++) {
std::cout << i << "番目の固有値:" << gsl_vector_get(eig, i) << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
//領域の開放
gsl_eigen_herm_free(workspace);
/////////////////////////////////////////
// 固有値と固有ベクトルの計算
/////////////////////////////////////////
// 作業領域の確保
gsl_eigen_hermv_workspace *workspace_v = gsl_eigen_hermv_alloc(DIM);
// 行列のコピー
gsl_matrix_complex_memcpy(matrix, frank_a);
// 固有値・固有ベクトルの計算
gsl_eigen_hermv(matrix, eig, eig_vecs, workspace_v);
// 置換インデックスの保存
gsl_permutation *perm = gsl_permutation_alloc(DIM);
gsl_sort_vector_index(perm, eig);
// 固有値の書き出し
std::cout << "-----固有値と固有ベクトルを計算-----" << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < DIM; i++) {
std::cout << i << "番目の固有値: " << gsl_vector_get(eig, gsl_permutation_get(perm, i));
std::cout << " 固有ベクトル: ";
for (int j = 0; j < DIM; j++) {
gsl_complex z_temp = gsl_matrix_complex_get(eig_vecs, i, j);
std::cout << GSL_REAL(z_temp);
if (GSL_IMAG(z_temp) >= 0) std::cout << "+";
std::cout << GSL_IMAG(z_temp) << "i ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
//領域の開放
gsl_permutation_free(perm);
/////////////////////////////////////////
// 計算チェック
/////////////////////////////////////////
// AX - EX == 0 ?
gsl_matrix_complex *tmp_matrix = gsl_matrix_complex_alloc(DIM, DIM);
// 単位行列に設定
gsl_matrix_complex_set_identity(tmp_matrix);
//固有値による対角ベクトルを準備(matrix)
for (int i = 0; i < DIM; i++) {
//実部と虚部
gsl_complex aa = { gsl_vector_get(eig, i) , 0 };
for (int j = 0; j < DIM; j++) {
gsl_matrix_complex_set(matrix, j, i, aa);
}
}
//EXを計算
gsl_matrix_complex_mul_elements(matrix, eig_vecs);
gsl_complex al = { 1.0, 0.0 };
gsl_complex beta = { -1.0, 0.0 };
//AX-EXを計算
gsl_blas_zgemm(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, al, frank_a, eig_vecs, beta, matrix);
std::cout << "検算 AX-XE = " << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < DIM; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < DIM; j++) {
gsl_complex z_temp = gsl_matrix_complex_get(matrix, i, j);
std::cout << GSL_REAL(z_temp);
if (GSL_IMAG(z_temp) >= 0) std::cout << "+";
std::cout << GSL_IMAG(z_temp) << "i ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
//領域の開放
gsl_matrix_complex_free(eig_vecs);
gsl_matrix_complex_free(tmp_matrix);
gsl_eigen_hermv_free(workspace_v);
gsl_matrix_complex_free(frank_a);
gsl_matrix_complex_free(matrix);
gsl_vector_complex_free(eig_vec);
gsl_vector_free(eig);
std::string s;
std::cin >> s;
return 0;
}
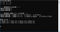
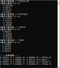
実行結果
いよいよ次はシュレディンガー方程式の固有値問題に取り組みます。